Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odorless, colorless gas that often goes undetected, striking victims at home and at work. At work sites all internal combustion engines, including diesel, gasoline, kerosene and propane-powered engines can produce dangerous levels of carbon monoxide. This includes forklifts, pressure washers, concrete cutters, water pumps, air compressors, generators, kerosene space heaters, natural gas cooking units, and propane-powered floor polishers. At home, this “invisible killer” is produced by burning fuel in cars or trucks, small engines, stoves, lanterns, grills, fireplaces, gas ranges, portable generators or furnaces.
Outdoor use of any of this equipment is not usually hazardous but in buildings or enclosed spaces, carbon monoxide can quickly build up to dangerous and even deadly amounts.
How Can I Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning at Home?
Winter can be a prime time for carbon monoxide poisoning as people turn on their heating systems and mistakenly warm their cars in garages. As the weather turns colder, it is important to take extra precautions.
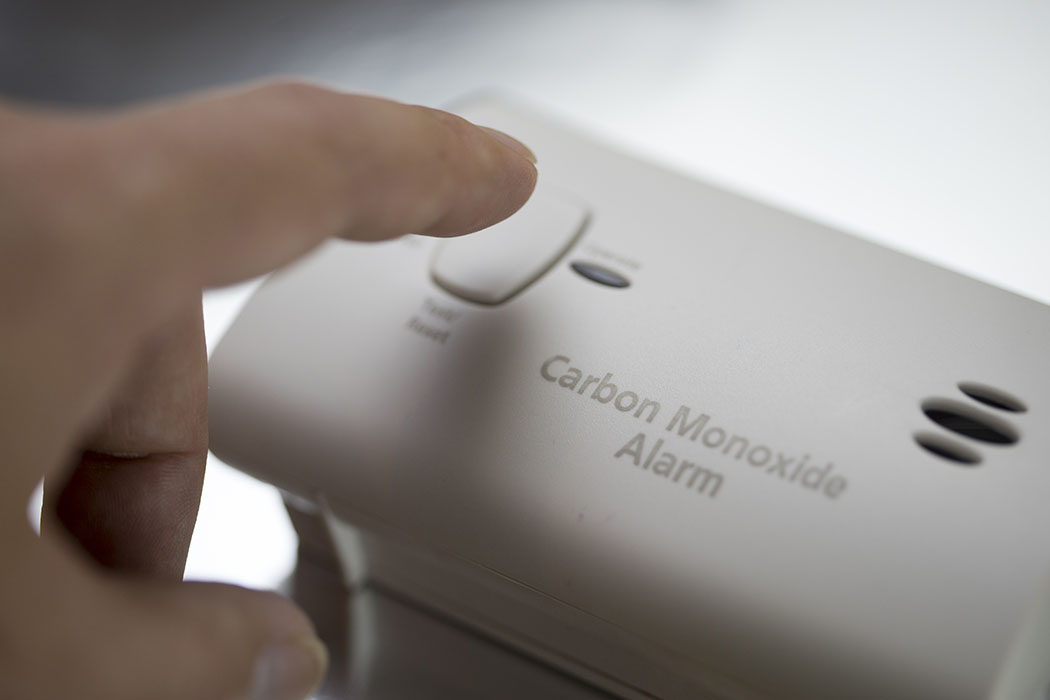
The National Safety Council recommends you install a battery-operated or battery backup carbon monoxide detector in the hallway near each separate sleeping area in your home. Check or replace the battery when you change the time on your clocks each spring and fall and replace the detector every five years.
The CDC offers these additional tips:
- Have your furnace, water heater and any other gas or coal-burning appliances serviced by a qualified technician every year.
- Do not use portable flameless chemical heaters indoors.
- Have your chimney checked and cleaned every year, and make sure your fireplace damper is open before lighting a fire and well after the fire is extinguished.
- Never use a gas oven for heating your home.
- Never use a generator inside your home, basement or garage or less than 20 feet from any window, door or vent; fatal levels of carbon monoxide can be produced in just minutes, even if doors and windows are open.
- Never run a car in a garage that is attached to a house, even with the garage door open; always open the door to a detached garage to let in fresh air when you run a car inside.
How Can I Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning at Work?
- Ensure that gasoline-powered pressure washers or other fuel-powered tools are not used in enclosed or partially enclosed areas where CO can build up.
- Install an effective ventilation system capable of removing CO from the work area.
- Train employees on the hazards, sources, symptoms, and control of CO exposure from fuel-powered equipment and tools.
- Use personal CO detectors equipped with audible alarms for employees who work with small gasoline-powered engines in locations where CO may build up.
- Attach CO safety warning labels to pressure washers and other potential equipment sources.
- Consider using alternatives to fuel powered equipment and tools.
When the Carbon Monoxide Alarm Sounds
The Consumer Product Safety Commission warns that you should never ignore a carbon monoxide alarm, and do not try to find the source of the gas. Instead, follow these steps:
- Immediately move outside to fresh air.
- Call emergency services, fire department or 9-1-1.
- Do a head count to check to account for everyone.
- Do not reenter the premises until emergency responders have given you permission to do so.




 ESD 112 equalizes educational opportunities for learning communities through innovative partnerships, responsive leadership, and exceptional programs.
ESD 112 equalizes educational opportunities for learning communities through innovative partnerships, responsive leadership, and exceptional programs.